About jewellery
Investment jewellery
It is the twenty-first century luxurious investment that was already known in ancient times and that was successfully implemented for thousands of years by successive generations of rulers and the high and mighty of this world. The investment doesn’t require any specialist knowledge of economics, doesn’t involve risk and allows easy transfer of capital to anywhere in the world. Exclusive jewellery is not only a beautiful ornament but also an excellent investment that combines the guaranteed stable value of precious metals and stones with elite artistic value of collectible works of art.
As a matter of fact, diamonds, gold, silver, sapphires, rubies and emeralds always maintain their actual value and are not subject to inflation. Their value doesn’t depend on economic crises, currency exchange rates and political turbulences. Just the opposite, during times of uncertainty, when all other components or our investment portfolio deprecate, their value increases.
Investment jewellery is a more reliable investment than bonds and more real than a bottle of wine and most importantly it can serve its purpose while not losing its value. Sceptics may say that purchase of raw materials is a better investment. But this is true only when it comes to large investments. Exclusive jewellery is an additional investment that is worth adding to our portfolio (preferably to 5% of its value). One can buy a diamond necklace instead of a bar of gold and present his loved one with it which will definitely make her happy. The necklace would become an ancestral good that can be handed down from generation to generation. Investment jewellery is also easy to sell when such need arises. It’s much easier to cross borders wearing a diamond necklace than carrying a bar of gold or a bag of diamonds in our pocket.
Staviori products are created by the greatest Italian goldsmiths. Every piece of jewellery is made with the highest precision. Diamonds and other precious stones are embedded under a microscope which guaranteed exceptional durability. Selling our products online allows us to maintain lowest prices which are crucial in jewellery investments.
Investment diamonds
Gemstones will always maintain their actual value which is not dependent on economic crises, turning points in history, currency exchange rates or falling prices of securities. Diamonds are comparable to a separate, universal currency not restricted by any borders.
THE ONLY PRECIOUS
Only few stones deserve to be called precious. These are: diamonds, ruby, emerald, sapphire, chrysoberyl and opal. Other natural stones that are less durable and softer are referred to as semi-precious stones. These include, for example, topaz, garnet, aquamarine, chrysolite, turquoise, zircon, tourmaline, hyacinth, spinel, amethyst, rock crystal and morion.
Although diamonds have always been a symbol of authority and power, real diamond fever began in the 19th century and it still continues. Large diamonds are one of the most precious jewels in the world. The largest diamond found in South Africa in 1905 had a mass of 3106 carats. It has been cut into 103 pieces and polished. The biggest piece of that diamond of 530.2 carats has been set into Queen’s sceptre. It’s called the Great Star of Africa (Cullinan diamond).
THE MOST VALUABLE
Diamonds are indisputable kings of gemstones; their name comes from the ancient Greek αδάμας – adámas "unbreakable". Diamond is an allotrope of carbon, where carbon atoms are evenly arranged. It is the hardest known material in the world. On the Mohs scale of mineral hardness it has a hardness of 10 (hardest). Diamonds have already survived 3 billion years in nature. The temperature of 1325°C and the pressure of 50 thousand kg/cm2 (comparable to placing the Eiffel tower on our hand) transformed carbon into this wonderful nature creation that will dazzle us with its shine till the end of the world.
INVESTING IN DIAMONDS
Gemstones’ prices increased significantly in recent years. Gemstone investment rates can be either high or low but will never bring loses. Polished diamonds cost anything between several hundred and several million dollars per carat. Their value is constantly increasing because of growing demand and limited supply. The amount of natural diamonds is limited and not all of those found are suitable for polishing.
NOBLE ALTERNATIVE
Traditional equity investments are becoming increasingly uncertain and global markets are no longer stable. The uncertainty of current economic situation contributed to the development of alternative forms of investment, among which diamonds are the most reliable form of saving. It is a real investment and not temporary virtual value recorded in registers of banks that may go bancrupt. The value of a gemstone depends more on its individual characteristics that on the market situation.
However, such investments require proper knowledge and caution; stones should be chosen with utmost care. We provide you specialist advice and help in choosing a perfect diamond. We can also create a unique piece of jewellery with your diamond because diamonds are meant to dazzle others rather than be locked away in a safe.
Gems can be purchased from specialist jewellery companies. This is the only way of buying that carries no risk of fraud, especially when a diamond comes with an international certificate of authencity issued by one of the 3 most important gemmological laboratories: HRD, IGI or GIA. The certificates are globally recognized and certified diamonds may be several times more expensive than not certified ones. Staviori makes every effort to ensure that stones we use are of the highest quality and their origins meet the UN criteria -that they come from countries free from armed conflicts.
HOW TO EVALUATE?
Diamonds price depends on 4 factors, known as “4Cs”: carat, clarity, colour and cut. The bigger the stone is the higher the value per carat gets. The price per carat of a 1,00-1,49 carat stone is on average 3 times higher than the price per carat of a 0,30-0,37 carat stone of the same colour and cut. Diamonds are classified by colour into classes D-Z. Clear ones are the most expensive (D to I), and yellow ones are classified J to Z. Prices of yellow diamonds can be several times lower than clear diamond prices. There are also blue, green, pink, brown and black diamonds.
Diamonds are the rarest natural minerals. The best diamonds come from Angola, Namibia and Russia. Raw diamonds are matt and dull. It is the polish that brings it to life. Only the best diamond cutters can shape it to make it glow and shine.
4C - DIAMOND CHARACTERISTICS
CARAT
The weight of a diamond is expressed in carats. One carat = 0,2 grams and one carat equals 100 points. Which means that 10 pointer diamond weights 1/10 of a carat usually denoted as 0.10 ct.
CLARITY
All diamonds have traces of their growth history. Microscopic inclusions are an integral feature of gemstones. The clarity scale reflects the size, number, location and visibility of the characteristics when examined with a loupe 10x. The very best and rarest clarity is loupe clean. Most inclusions, however, are not visible to the naked eye. Diamonds that have no inclusions visible to the unaided eye are also of excellent value.
COLOUR
Most diamonds are colourless to slightly yellowish. The colour grade is determined by comparison with a series of masterstones, the best grade being colourless. With an exception of intense colours such as pink or light blue which are also very valuable. Diamonds can occur in all sorts of colours, ranging from brownish to striking yellows, purple, red and blue. These are called “fancy colours”
CUT
Brilliant cut diamonds are referred to as round diamonds. Other popular shapes are oval, marquise, pear, heart, emerald and princess. Diamond cut quality is determinative for the brilliancy and the fire of the diamond. Full cut diamond has 58 facets ( 56 facets, table and culet.) Low quality cut can depreciate the value of a stone even more then 50%. Evaluation of the cut is the most crucial part in diamond evaluation process.
Sapphire, ruby, emerald ...
SAPPHIRE
Sapphire is a variety of corundum, the next hardest natural stone after diamond. It’s usually but blue there are stones in all colours except red. The blue colour comes from iron and titanium. Some sapphire varieties get asterism from the titanium dioxide impurities present in them. The most precious sapphires are blue and come from Kashmir, Burma and Thailand. Stones from Sri Lanka are brighter and those from Australia are darker, often greenish.
RUBY
Rubies are a form of corundum. Their colour can by anything from bright red to almost purple shade of red. Their red colour comes from chromium. Like sapphires, these precious stones get asterism. The most precious rubies are red with a shade of blue. This colour is characteristic to rubies coming from Burma. Rubies have always been highly valued. Beautiful, large stones can be much more expensive than diamonds. Rubies can be found in Burma, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Tanzania an Afghanistan.
EMERALD
Emerald is a green, the most valuable type of beryl. Emeralds, as well as diamonds, sapphires and rubies are one of the most durable materials known to mankind. It’s mostly light to dark green, sometimes grass green. Its colour comes from admixture of chromium and vanadium. Value of emeralds is based on their beautiful colour and transparency. The most expensive emeralds are dark green, with no cracks or cloudiness. Large, unblemished stones can be more expensive than diamonds. Until the 19th century global market was dominated by Colombian emeralds. Their deposits were later discovered in the Urals, US, Austria, South Africa, India and Zimbabwe.
Gold info...
GOLD JEWELLERY
The oldest gold jewellery is about 6000 years old. Our jewellery will be equally old in 6000 years’ time! Goldsmithing flourished in Europe in the 16th and 17th century when jewellery in similar style was produced. Our design is unique and unrepeatable.
WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ?
Gold is a relatively soft metal so it’s alloyed with other metals, such as silver, zinc, copper and palladium. They not only make the gold harder, but also change its colour and smooth its surface. Gold’s assay indicates percentage of pure gold is in the alloy. For example 0,585 assay means than in 1000 units of alloy’s mass there are 585 units of pure gold. Until early 20th century gold was mostly assayed in carats. According to this system, gold 0,585 assay is 14 carat gold, 0,750 equals 18 carats and 0,333 equals 8 carats. Pure gold theoretically is 1000/1000; however, as it’s impossible to remove all impurities, the purest gold is 0.999. Gold with this assay is considered pure, 24 carat gold.
Gold’s colour doesn’t affect its price and is simply a result of colour enhancing treatment that consists of increasing the amount of other elements in the alloy. For example white gold has more silver in it than palladium and copper. The most popular colours are yellow, white, pink and red.
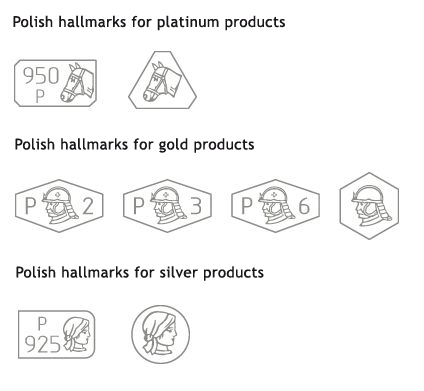
Under current law, all platinum, gold and silver products must be hallmarked. Hallmark must include the type of precious meal and its purity. Gold products of mass less than 1g and silver product of mass less than 5g don’t have to be hallmarked. Fine jewellery of a higher mass may be sold without hallmark if it is so delicate that hallmarking would damage it. Such jewellery should only be sold with an appropriate certificate that includes information on piece’s mass and purity of the material used. Some jewellery may have a laser hallmark.
Silver info...
SILVER JEWELLERY
The oldest known silver jewellery is about 22000 years old. Jewellery that we sell is definitely from the 21st century! In ancient times jewellery was used not only as an ornament but also as a tool of witchcraft. This is still the case today – our jewellery will enchant your world!
WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ?
Silver is extremely malleable (only slightly harder than gold), shiny and easy to polish. It has the best electrical conductivity of all metals. Pure silver has the best thermal conductivity, the brightest colour and the highest light reflectance. It was already known in the antiquity, valued as a precious metal and often used as a currency. To this day it is one of the most popular metals used by jewellers.
The only available silver on the Polish market is hallmarked 0,925, which means that in 1000 alloy mass units 925 are pure silver. Relatively low price in comparison to platinum and gold makes it ideal material for jewellery making. It can take many different forms and suits perfectly all kinds of beads, zirconia, coloured stones and enamel. Silver can be gold plated or rhodium-coated.
Natural rhodium is extremely rare. It is silver-grey; resistant to water, air and acids which makes rhodium-coated jewellery more durable. Rhodium coating is used in gold and silver to increase their hardness, enhance shine and develop resistance to weather, as well as to emphasize and maintain the bright whiteness of white gold. Unfortunately, rhodium coating on jewellery can wear off after a few years of use and it might be worth re-coating it in a reputable goldsmith’s workshop.
Hallmarks
Engagement ring
ENGAGEMENT RING
The Roman custom of giving an engagement ring to guarantee the completion of the contract of marriage has been legitimized by the church, and then, in the beginning of the 19th century, popularized. Medieval Italians honoured diamonds as a symbol of the engagement and harmony between husband and wife.
The perfect engagement ring is a single stone diamond ring. A classic example of such a ring is called chaton – simple and neat design with a single stone of any size in a delicate frame.
Ideal diamond is one that meets expectations of the buyer and the person to whom it is to be given. It is important to choose the right stone, in accordance with the “4Cs” criteria. Diamond’s size should be balanced with its quality; a happy medium is a diamond in colour H (white) and clarity Si (small inclusions invisible to the naked eye).
SIZE
The most popular size of women’s engagement ring and wedding band is M (both to be worn on the ring finger), and men’s is T. Staviori uses typical ring sizes based on diameter or circumference of your finger.
IMPORTANT! Please bear in mind that home made measurements are never going to be precize and you cannot rely on them 100%. In order to find out the correct size it is adviced to to measure the finger on which the ring will be worn, using specialized measuring tool. Please ask our Consultants.
Staviori offers standard ring sizes K-Q. In case of non standard sizes please contact us to determine price and delivery time.
RING SIZES
HOW TO DEFINE A RING SIZE?
1. Measure the diameter of any other ring that fits a given finger. Read out the ring size that matches the diameter.
2. Measure a finger’s circumference. Read out the size matching the circumference.
Please remember that ring sizes are measured up to 1/10 of millimeter. So the difference between two adjacent sizes might be so small that insignificant and be in the measurement – ballpark.
| Ring
sizes Poland | Ring sizes UK | Ring sizes USA | Inside diameter
in millimeters | Inside circumference in millimeters |
| 5 | G | 3¼ | 14.30 mm | 45 mm |
| 6 | H | 14.60 mm | 46 mm | |
| 7 | H½ | 4 | 15.00 mm | 47 mm |
| 8 | I½ | 4½ | 15.30 mm | 48 mm |
| 9 | J | 15.60 mm | 49 mm | |
| 10 | K | 5¼ | 15.90 mm | 50 mm |
| 11 | L | 16.20 mm | 51 mm | |
| 12 | L½ | 6 | 16.50 mm | 52 mm |
| 13 | M½ | 6½ | 16.80 mm | 53 mm |
| 14 | N | 17.20 mm | 54 mm | |
| 15 | O | 7¼ | 17.50 mm | 55 mm |
| 16 | O½ | 7½ | 17.80 mm | 56 mm |
| 17 | P½ | 8 | 18.10 mm | 57 mm |
| 18 | Q | 18.40 mm | 58 mm | |
| 19 | R | 18.80 mm | 59 mm | |
| 20 | S | 9¼ | 19.10 mm | 60 mm |
| 21 | S½ | 9½ | 19.40 mm | 61 mm |
| 22 | T½ | 10 | 19.70 mm | 62 mm |
| 23 | U | 10¼ | 20.00 mm | 63 mm |
| 24 | V | 20.30 mm | 64 mm | |
| 25 | V½ | 11 | 20.60 mm | 65 mm |
| 26 | W½ | 11½ | 21.00 mm | 66 mm |
| 27 | X½ | 12 | 21.30 mm | 67 mm |
| 28 | Y | 21.60 mm | 68 mm | |
| 29 | Z½ | 22.00 mm | 69 mm | |
| 30 | 13 | 22.30 mm | 70 mm | |
| 31 | Z+2 | 13½ | 22.60 mm | 71 mm |
Typical bracelet and necklace sizes
Every range of jeweller has its most common and most sought after sizes:
Women’s chain – length – 450mm (also 420mm and 500mm)
Women’s necklace – length – 420mm
Women’s bracelet – length – 190mm (also 180mm and 210mm)
Men’s chain – length – 550 mm (also 500mm and 600mm)
Men’s bracelet – length – 210mm to 230mm

How to care about jewellery...
RESPECT YOUR JEWELLERY
Authentic gold or silver jewellery, especially one with precious stones, is like a dress from Chanel so treat it with respect.
Gemstones and natural pearls are particularly vulnerable to loss, cracking, chipping, being treaded down or other damages caused by everyday use. You should take off your jewellery when you are doing housework, going to bed or exercising.
You should be careful when wearing fine, delicate chains. They can be damaged or deformed by a slight pull, even during sleep. When you take off your chain remember not to curl it or bend it too tight as it may cause a permanent deformation.
HOW TO CARE FOR YOUR JEWELLERY ?
1. The beauty of jewellery is durable, but also delicate and fragile. You can enjoy the glow of your favourite jewellery for a long time if you follow simple rules. Most jewellery can be damaged by direct contact with water. Water can affect jewellery is different ways; it may lose its shine or discolour. This applies particularly to pearls and mother of pearl as they are exceptionally delicate and sensitive. Getting marcasite jewellery wet can result in stones falling out. You should always remove all your jewellery before bathing or washing up.
2. Detergents in cleaning products and personal care products like hair sprays, deodorants and perfumes can cause discolouration. Jewellery is made either of pure metal or alloy of different metals that can react with various substances. Chemical products can harm natural or organic stones (pearls, ambers) by tarnishing them or causing delamination. Therefore, you should protect your jewellery from a direct contact with such substances by, for example, applying beauty products before putting on your jewellery.
3. Storing jewellery is also very important. Each piece should be wrapped in a soft cloth and sealed in a separate bag. It will help to avoid damage and exposure to dust etc. A good place to store your jewellery is a jewellery box. It is also recommended to have our jewellery professionally cleaned from time to time.
4. The best thing you can do at home is dust your jewellery regularly. It’s best to use special jewellery wipes. You shouldn’t attempt to clean your jewellery using cleaning product or polishes.

 (0)
(0)